There can be different ways in which the physician and patient can manage breast cancer or ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. The patient and oncologic surgeon or team of physicians may choose lumpectomy, or, conversely they may choose mastectomy.
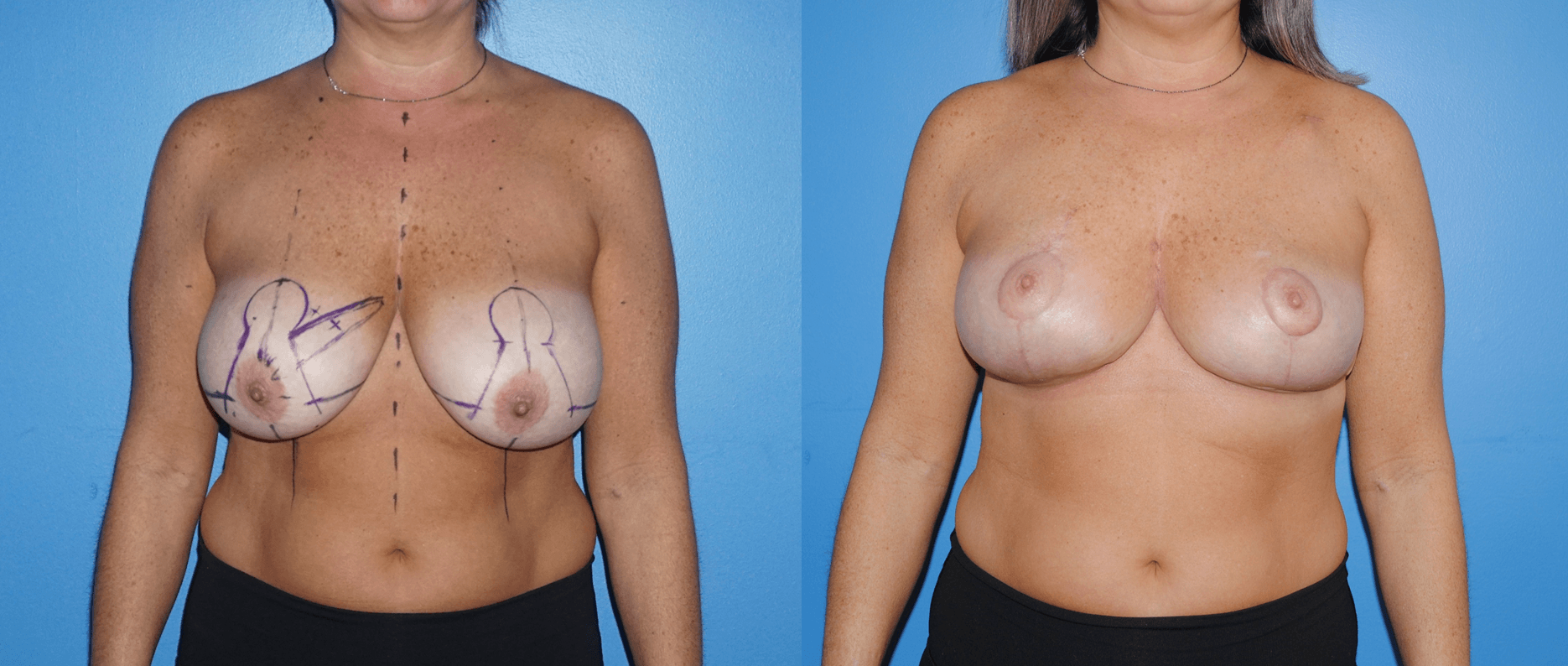
If a patient chooses a lumpectomy, the patient and reconstructive team can often reconstruct the breast with the patient’s own breast tissue. The terminology used to describe this type of reconstruction is oncoplastic reconstruction following lumpectomy.
In this type of reconstruction, the same patterns used to lift the breast or reduce the breast in an aesthetic mastopexy or breast reconstruction can be used by the oncologic team to remove a cancer or ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Breast tissue can then be rearranged to fill defects created by the lumpectomy and/or in conjunction Biozorb may be used to help fill a defect and or guide treatment and surveillance post-operatively.
Lumpectomy for the treatment of breast cancer is often followed by radiation therapy. The change in shape of the breast to a more youthful appearance can also facilitate the delivery of radiation. The more compact volume and surface area and obliteration of dead space, can make radiation delivery more effective.