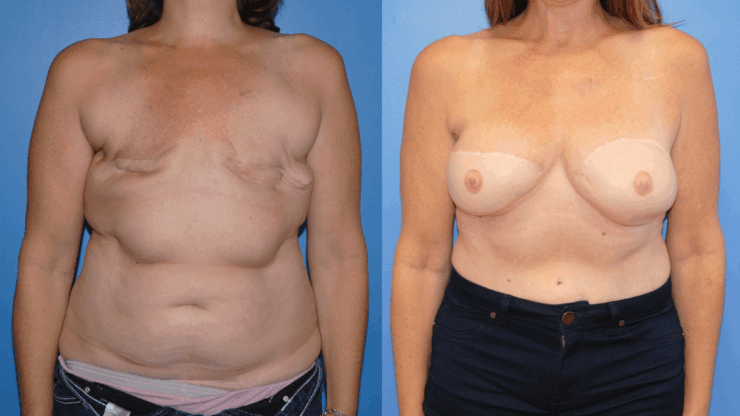
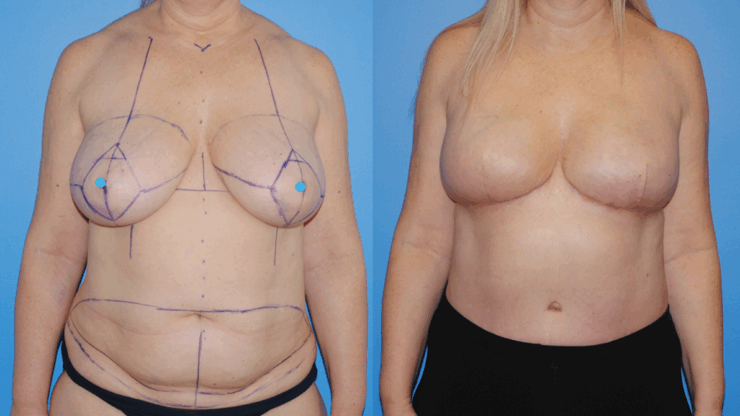
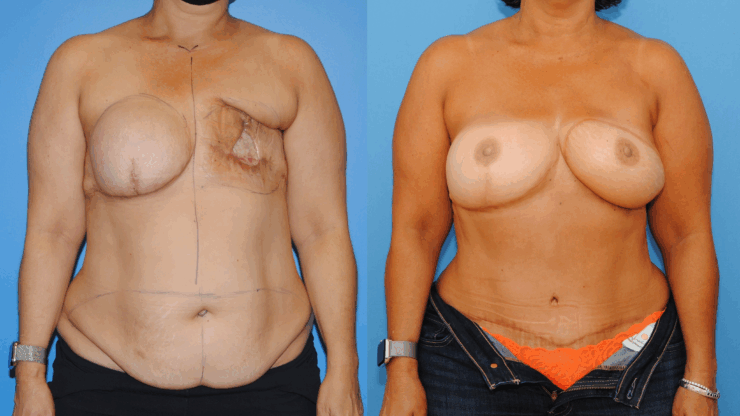
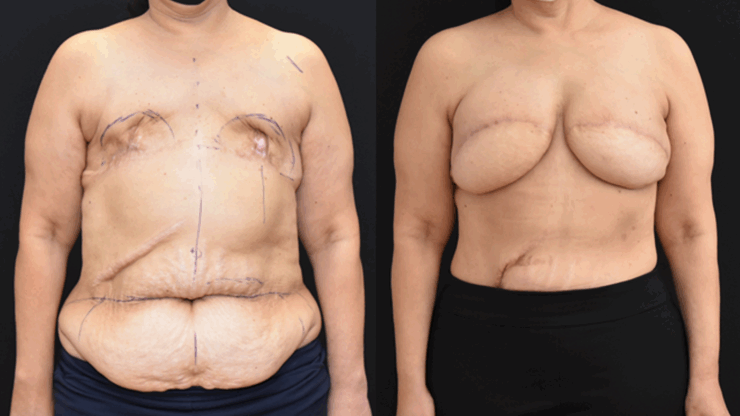
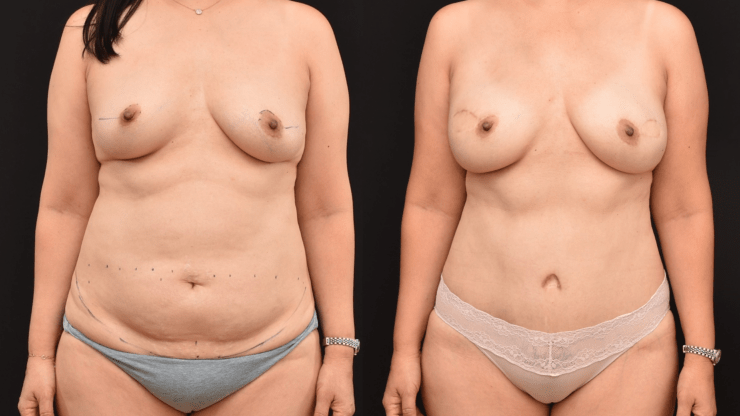
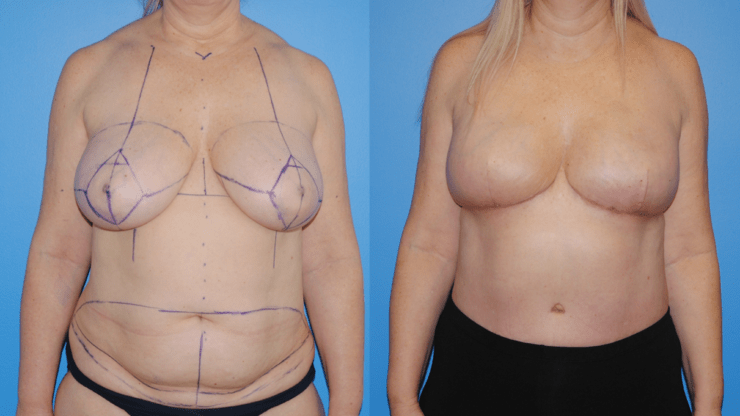
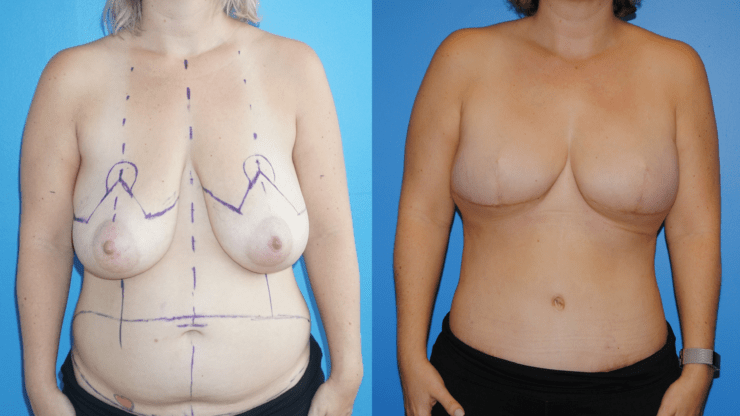
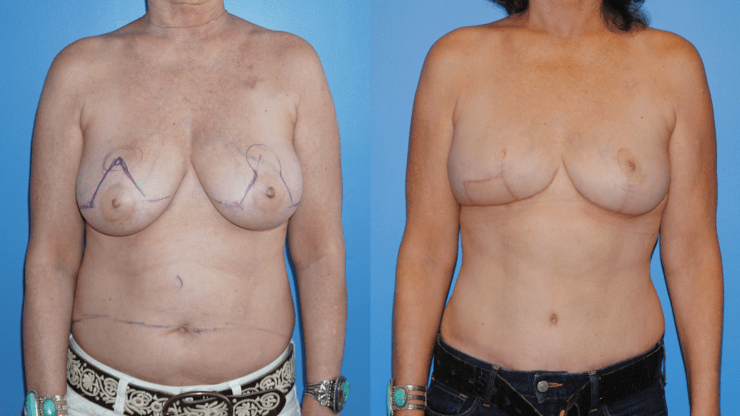
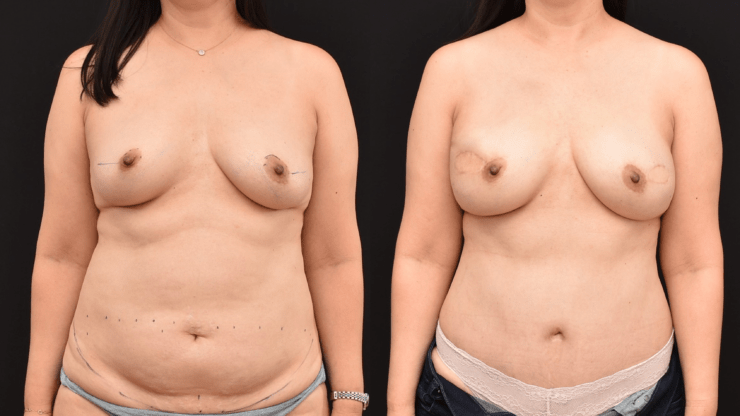
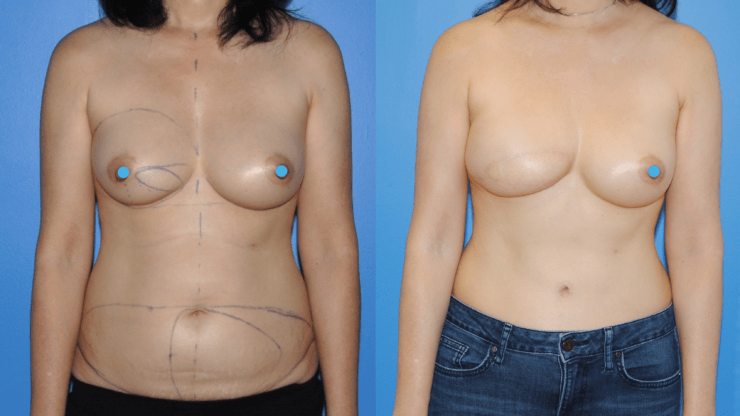
October is Breast Cancer Awareness Month. Breast cancer reconstruction can occur in a delayed fashion-meaning at a time remote since the date of mastectomy. When the skin of the breast has been radiated or if it is significantly scared from infection, the breast can often be reconstructed with skin and fat from the abdomen. This operation is called DIEP flap…