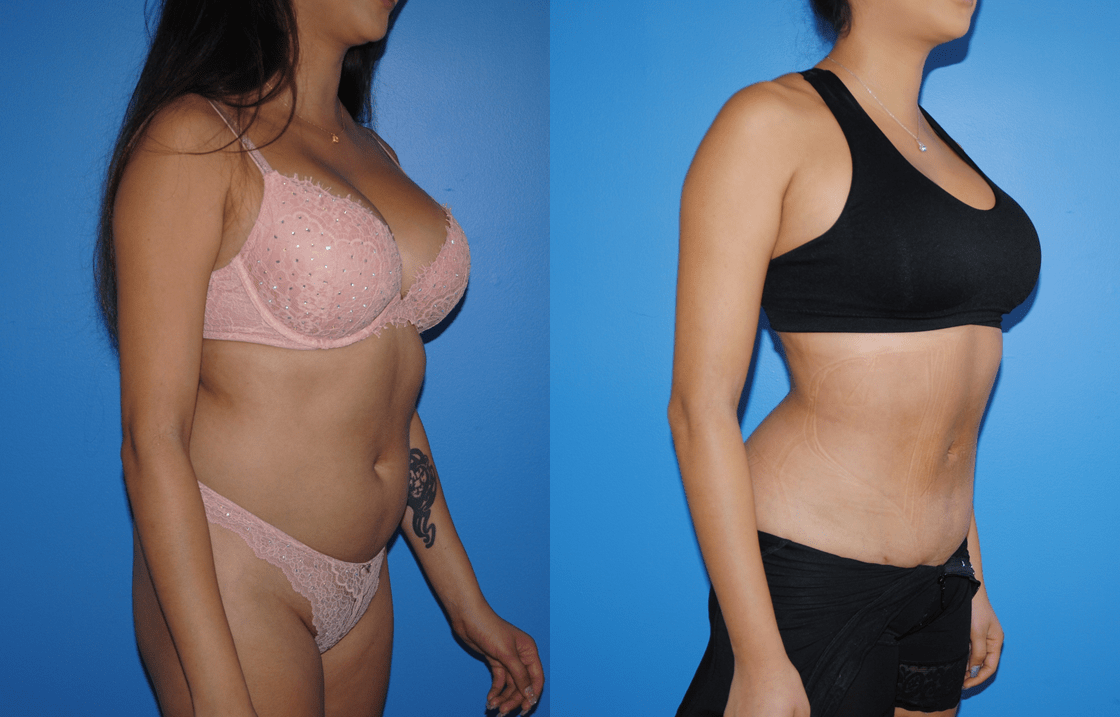
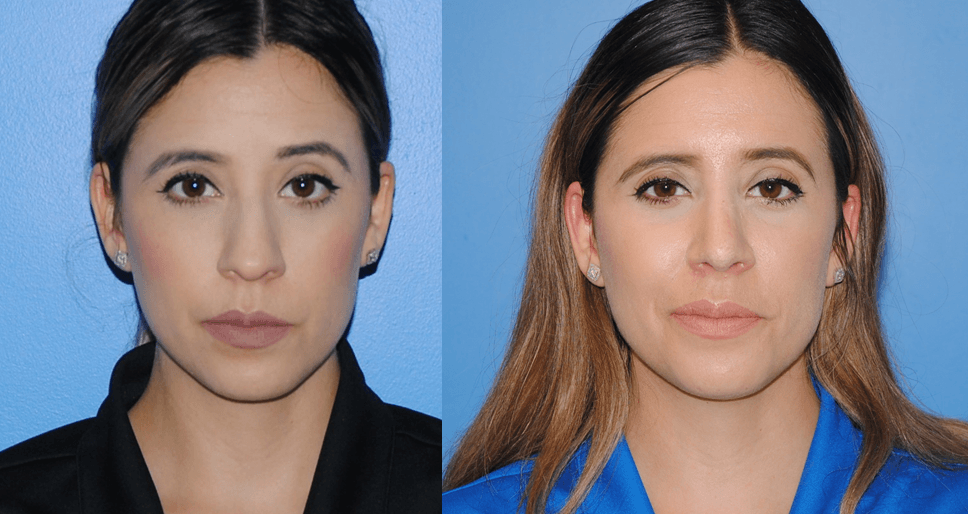
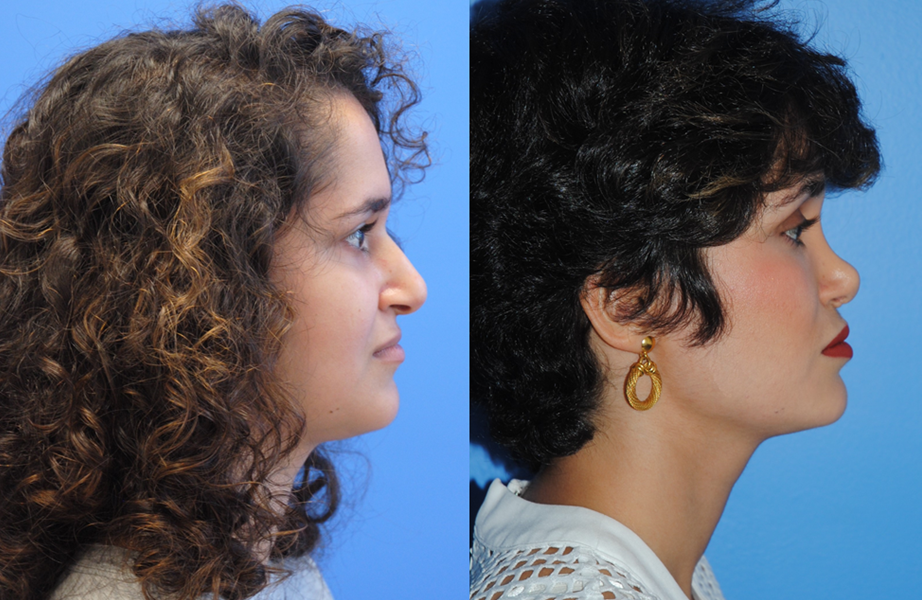
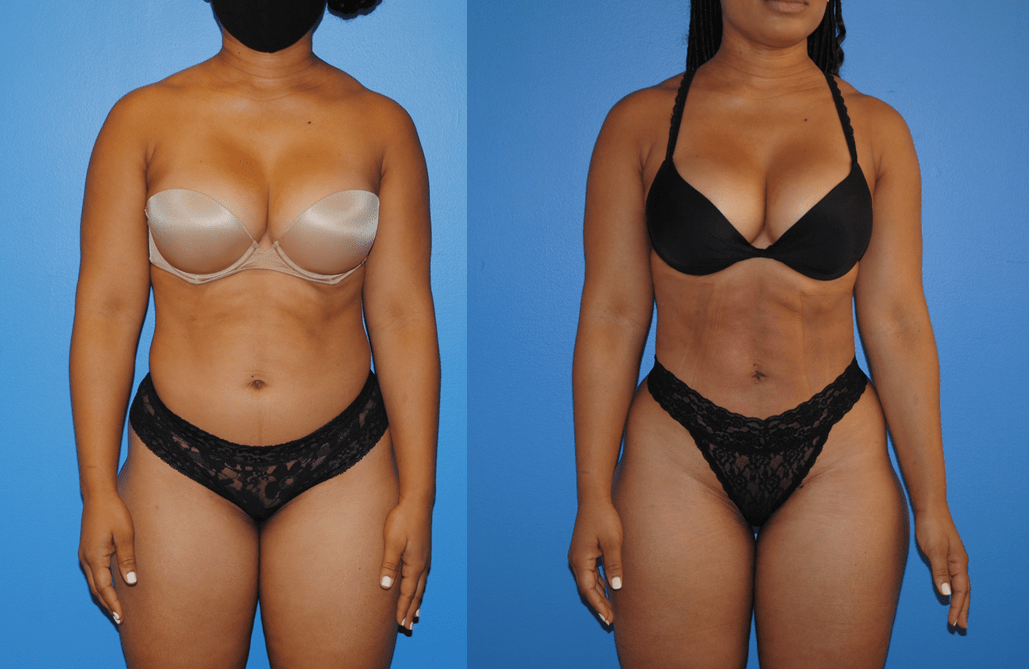
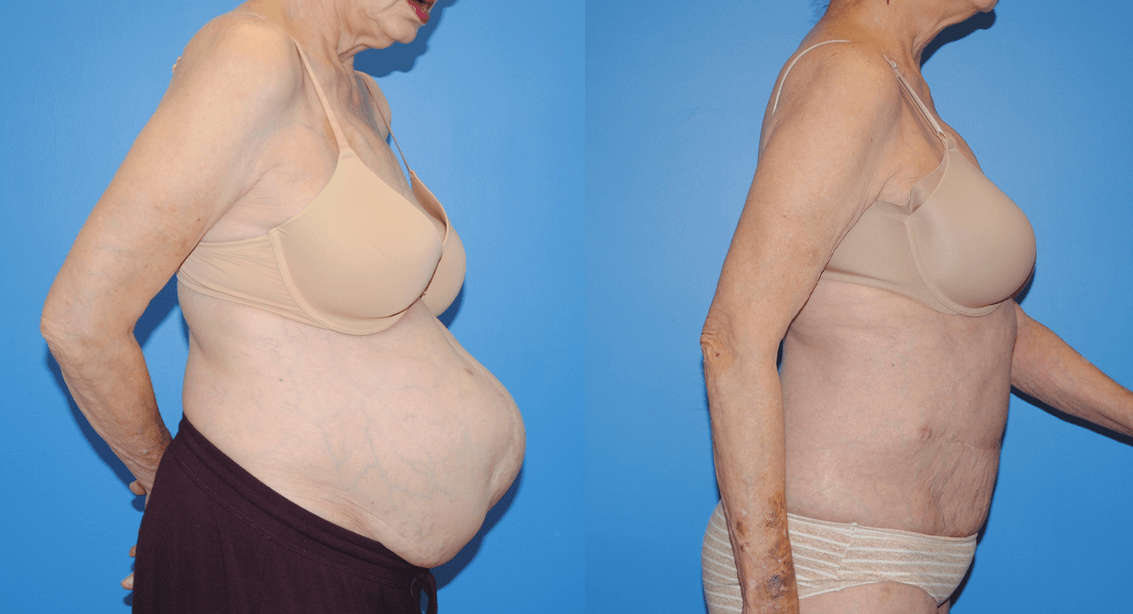
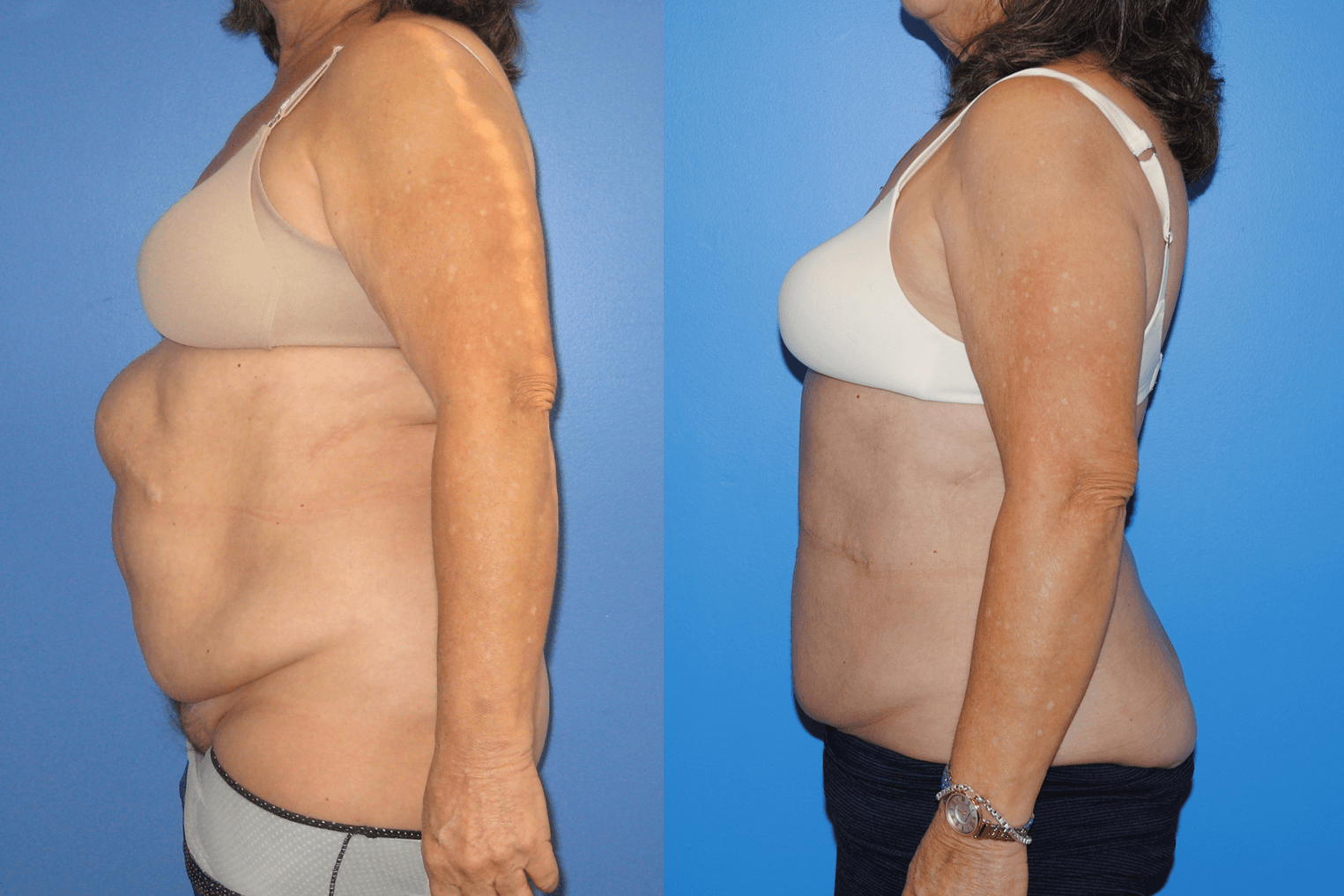
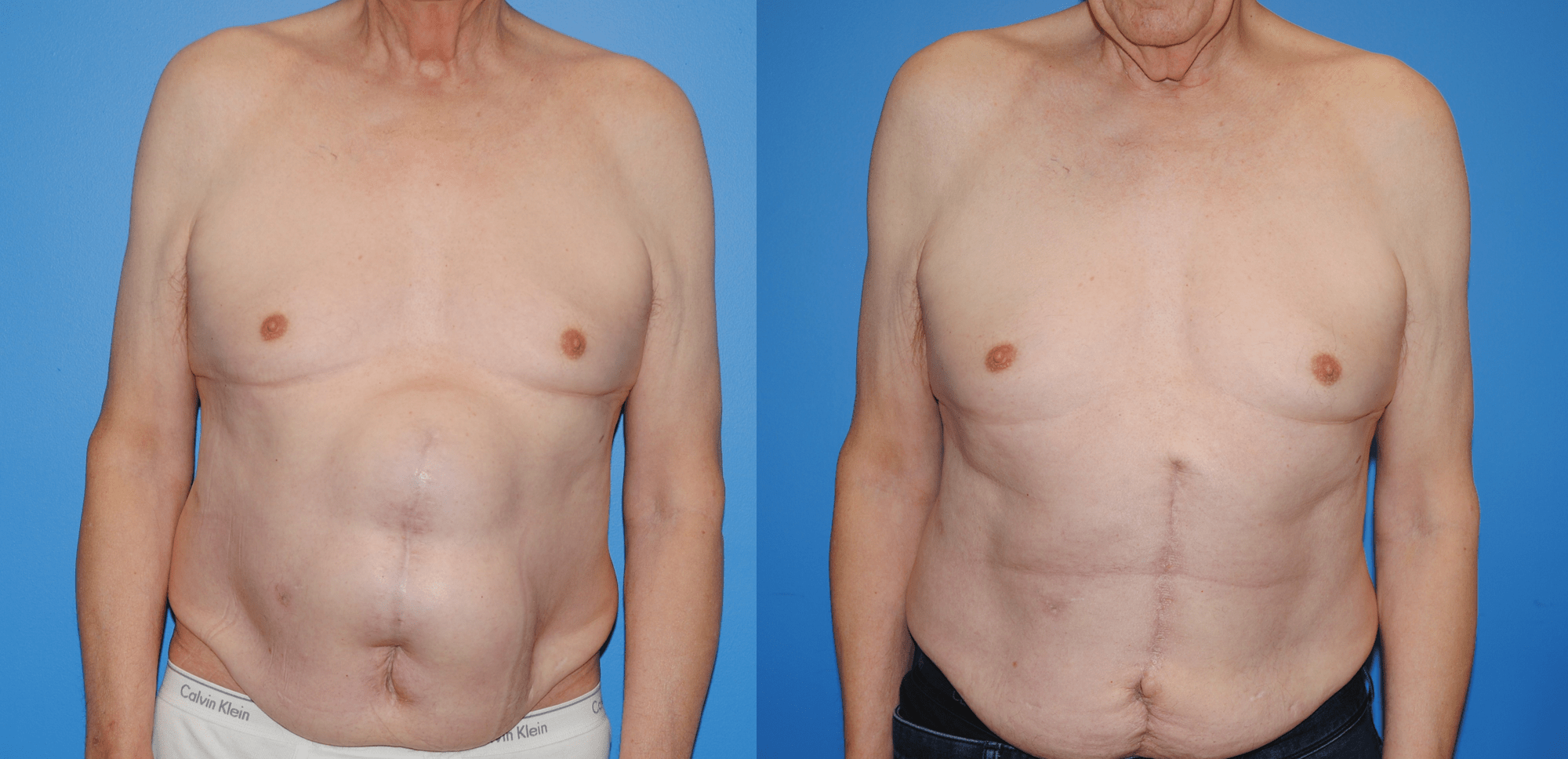
Gluteal fat transfer can be very rewarding for the patient. Patients who have a high satisfaction rate have lower lumbar lipodystrophy as well as a lordotic spine posture. Patients wear a compression garment, abdominal binder, and/or faha beneath the compression garment. The more compliant patients are with the compression garments, the better results they acheive. Patients are allowed to sit…