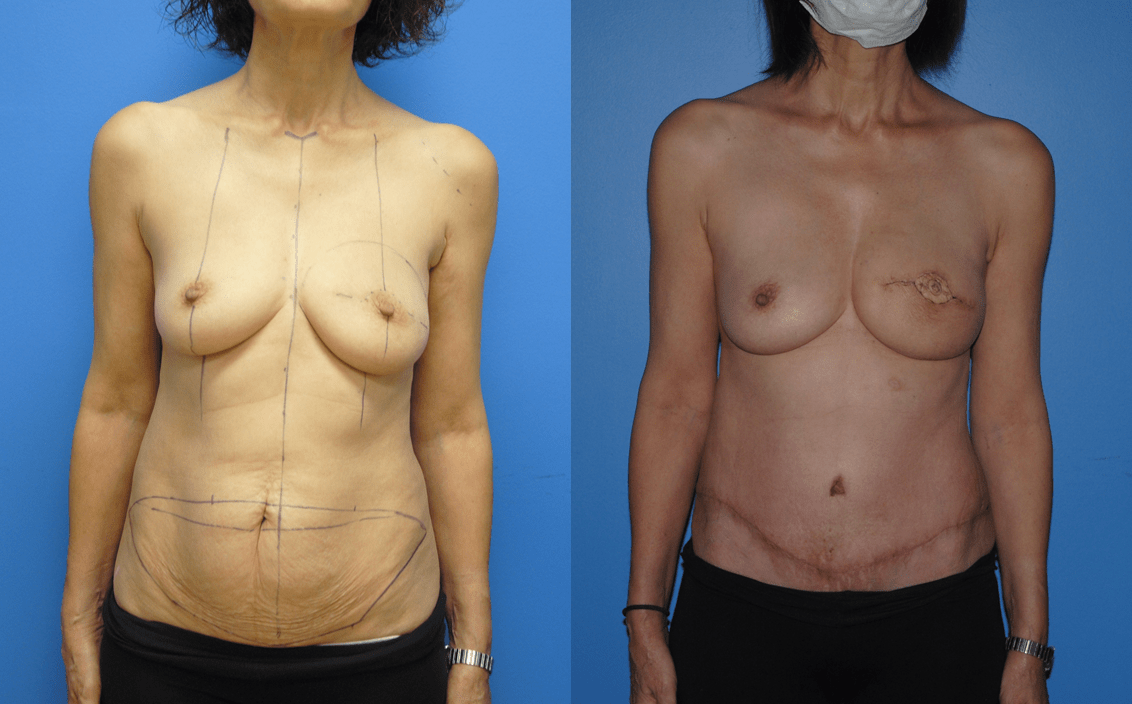
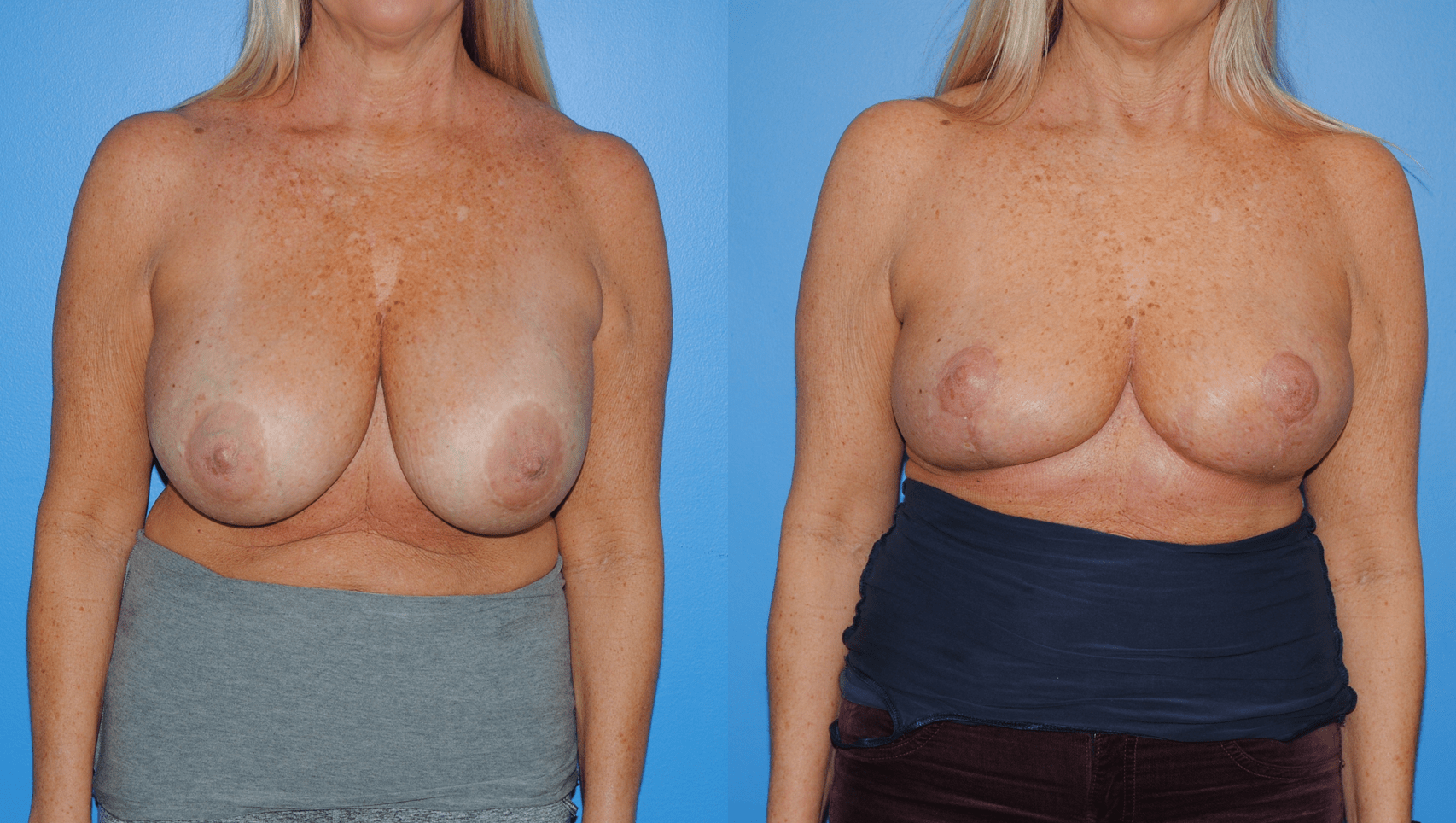
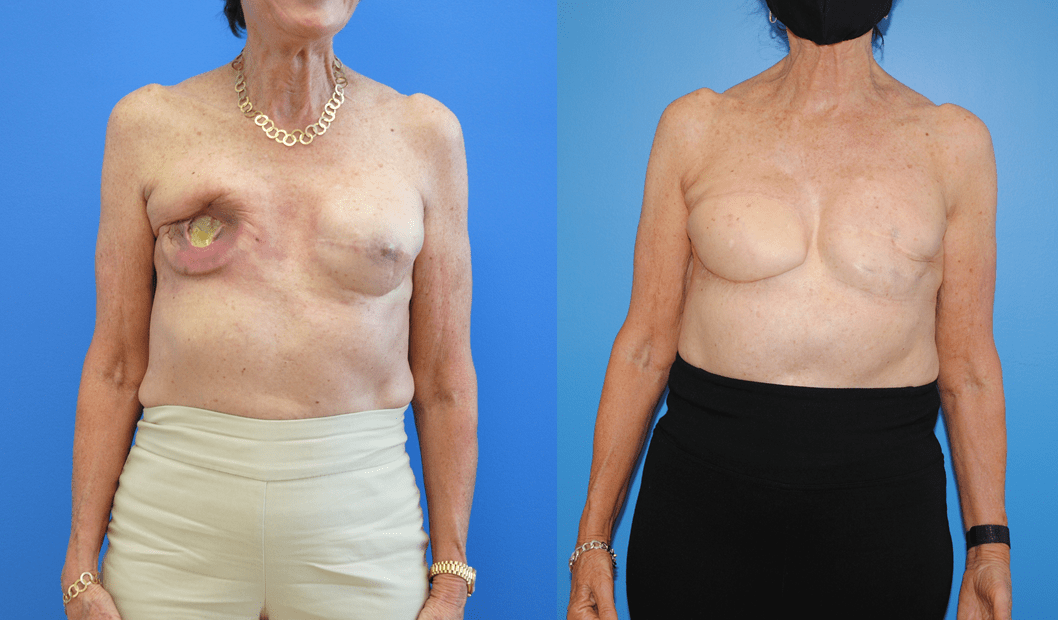
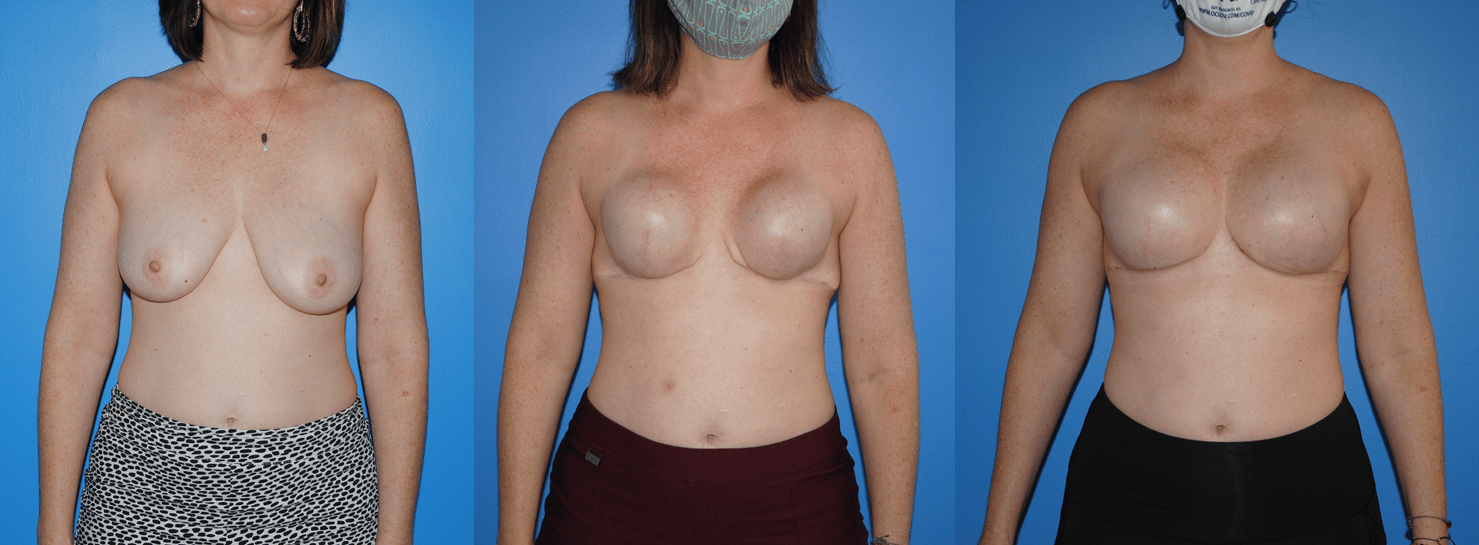
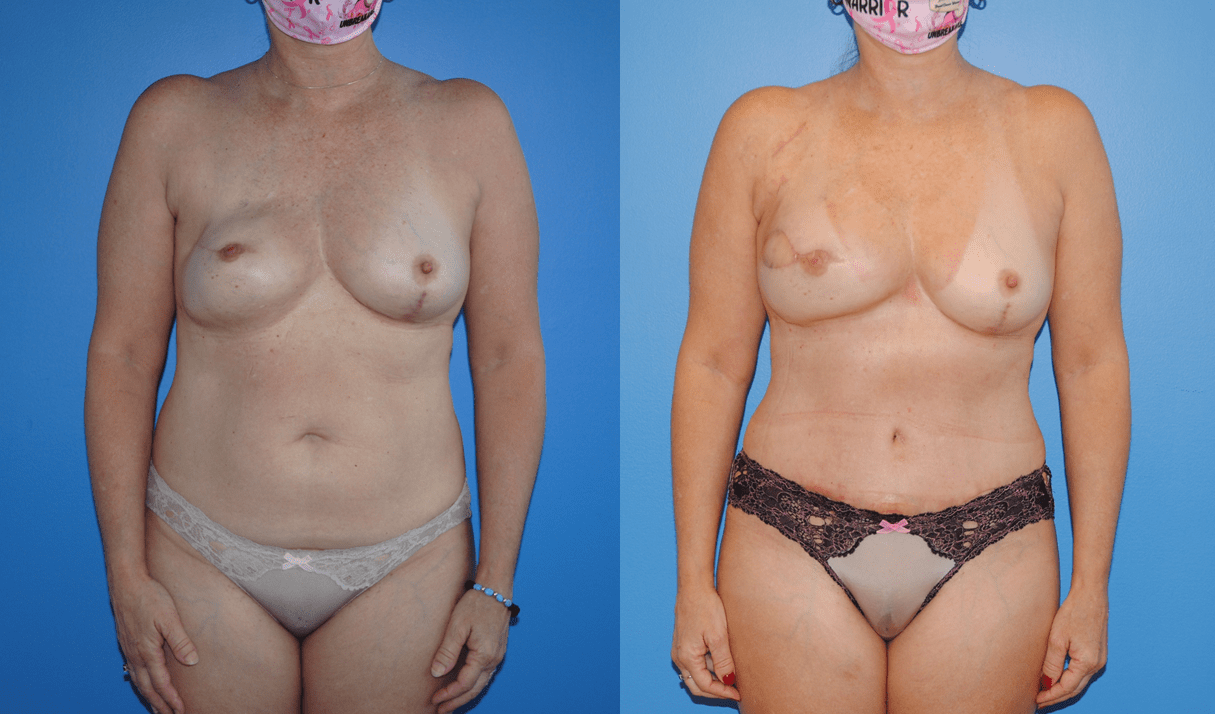
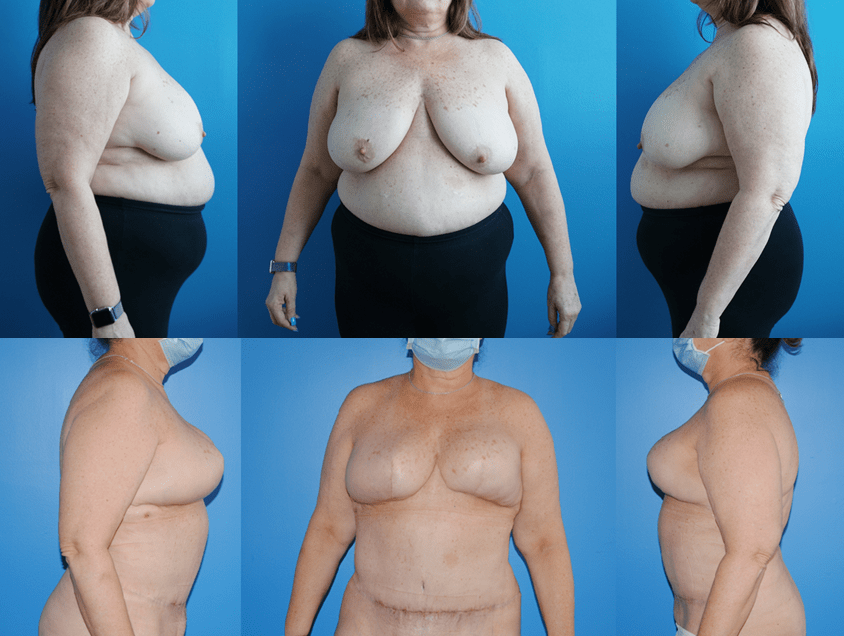
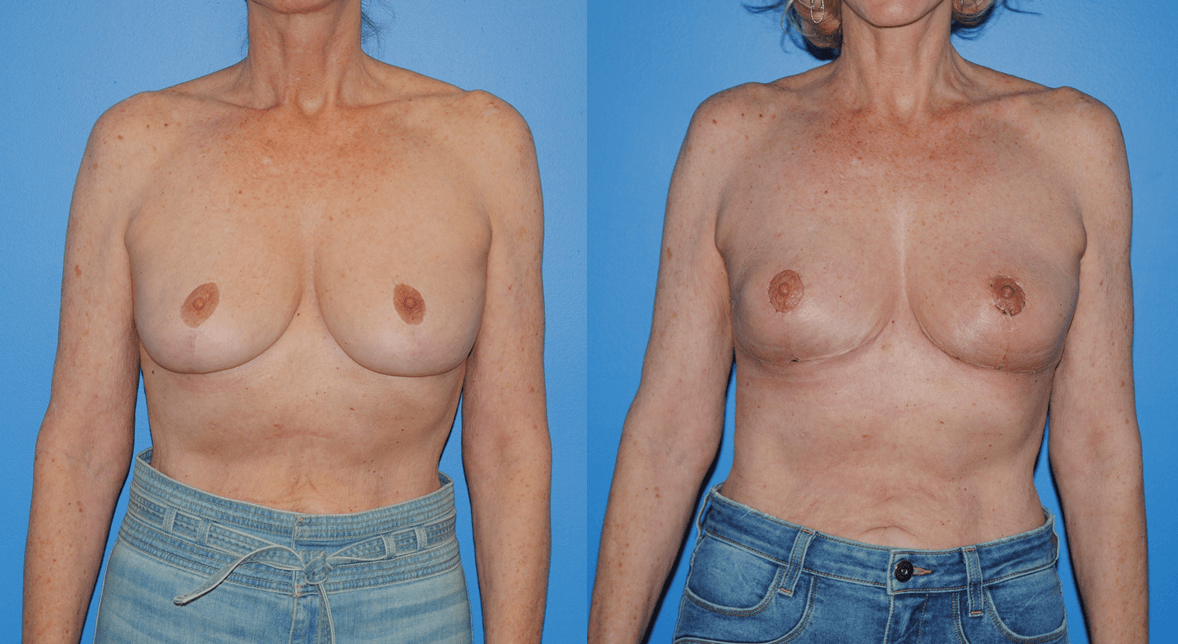
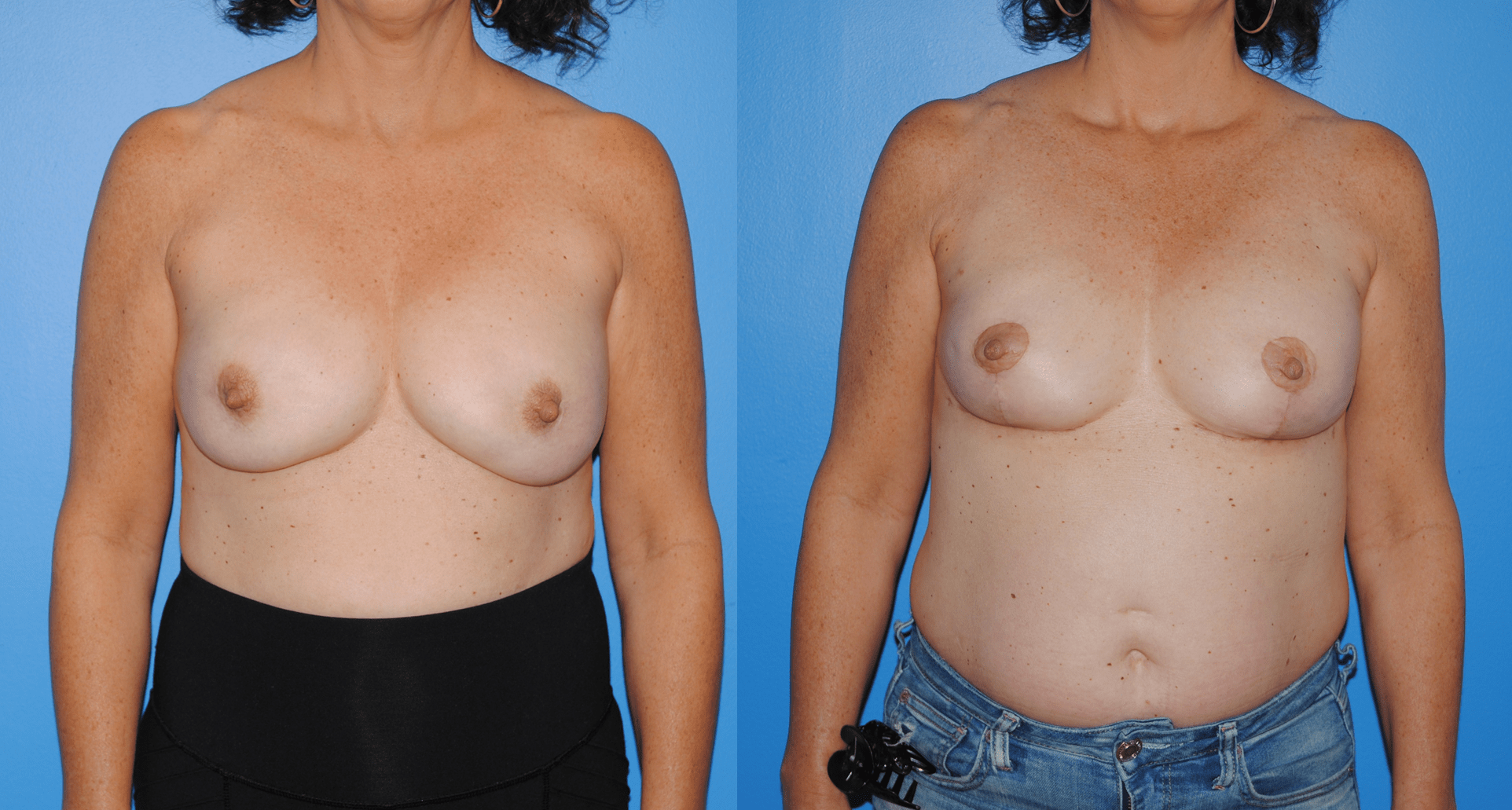
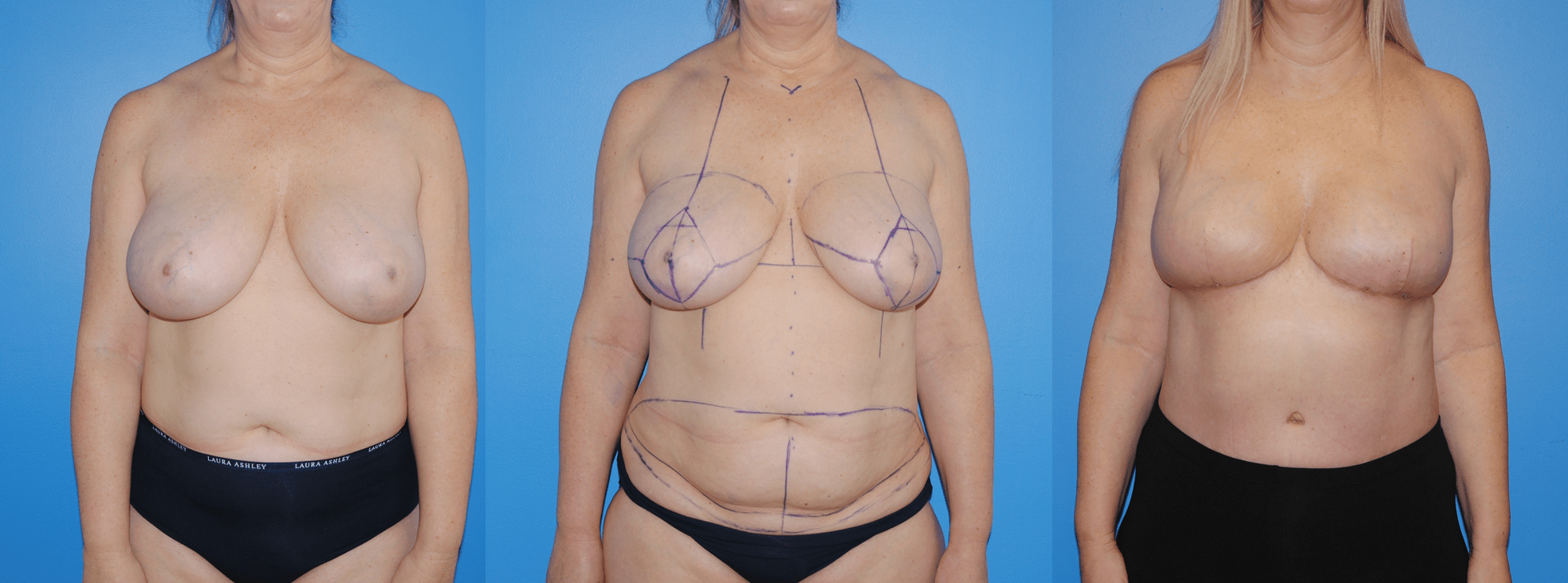
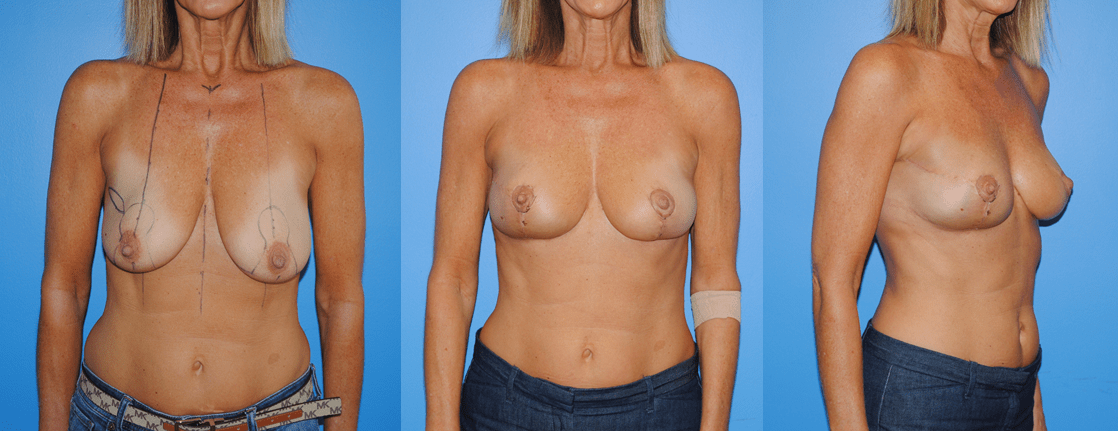
Patients will frequently ask if it is possible to undergo mastectomy reconstruction if they have had previous lumpectomy and whole breast radiation. There are different options for patients who undergo previous radiation therapy. If there is ample tissue present on the abdominal wall, the lower abdomen can serve as the donor site for tissue to be transferred to reconstruct the…