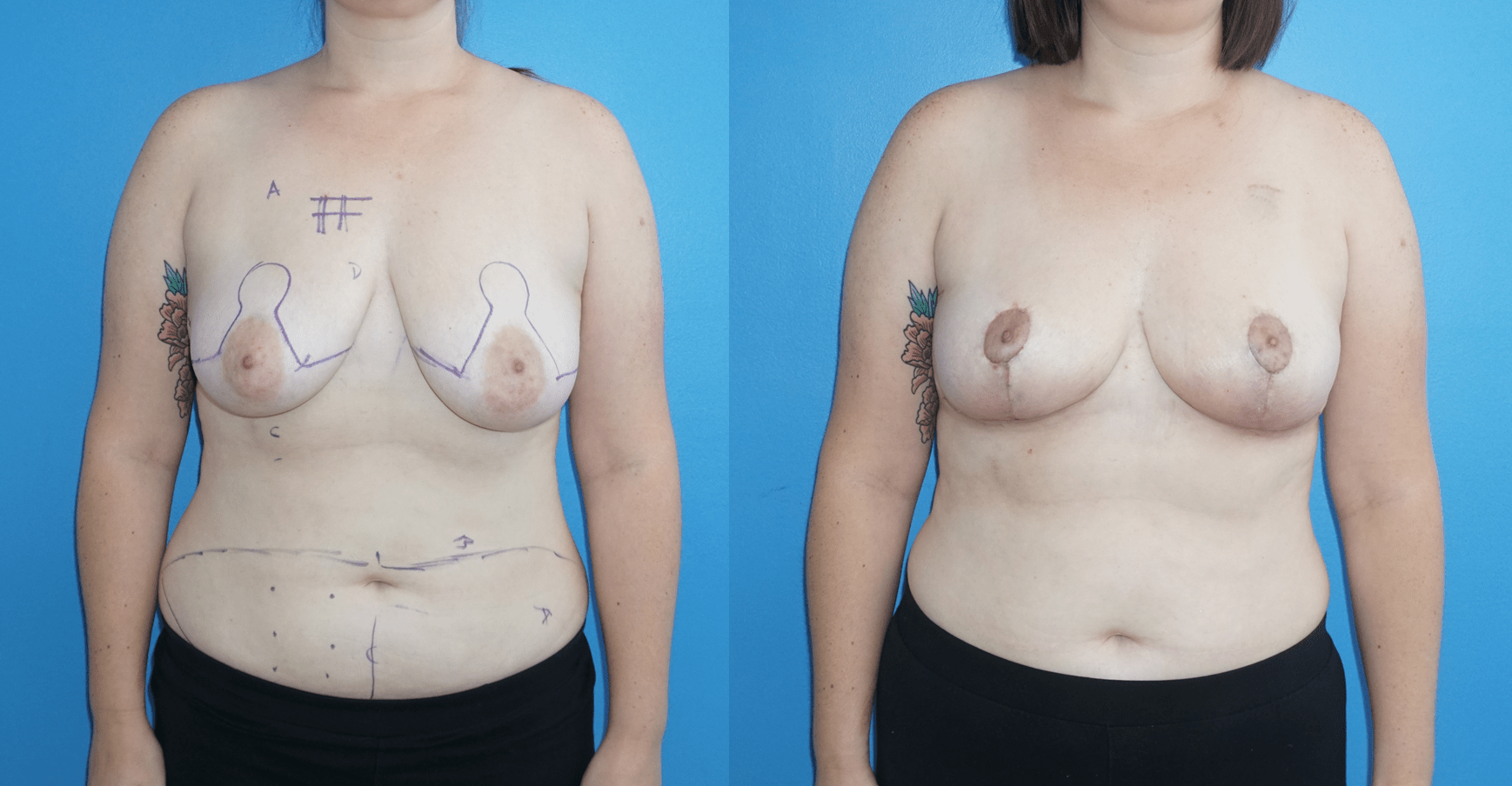
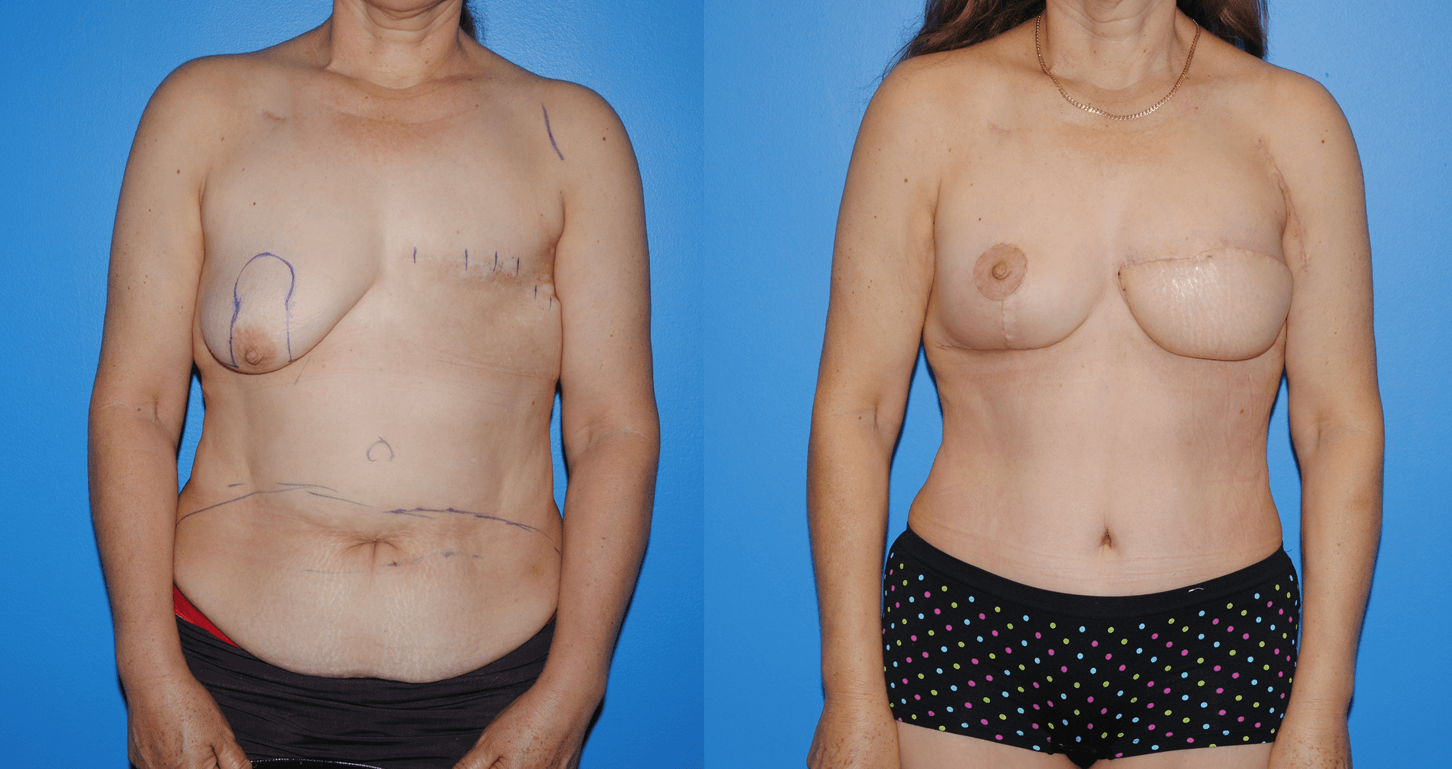
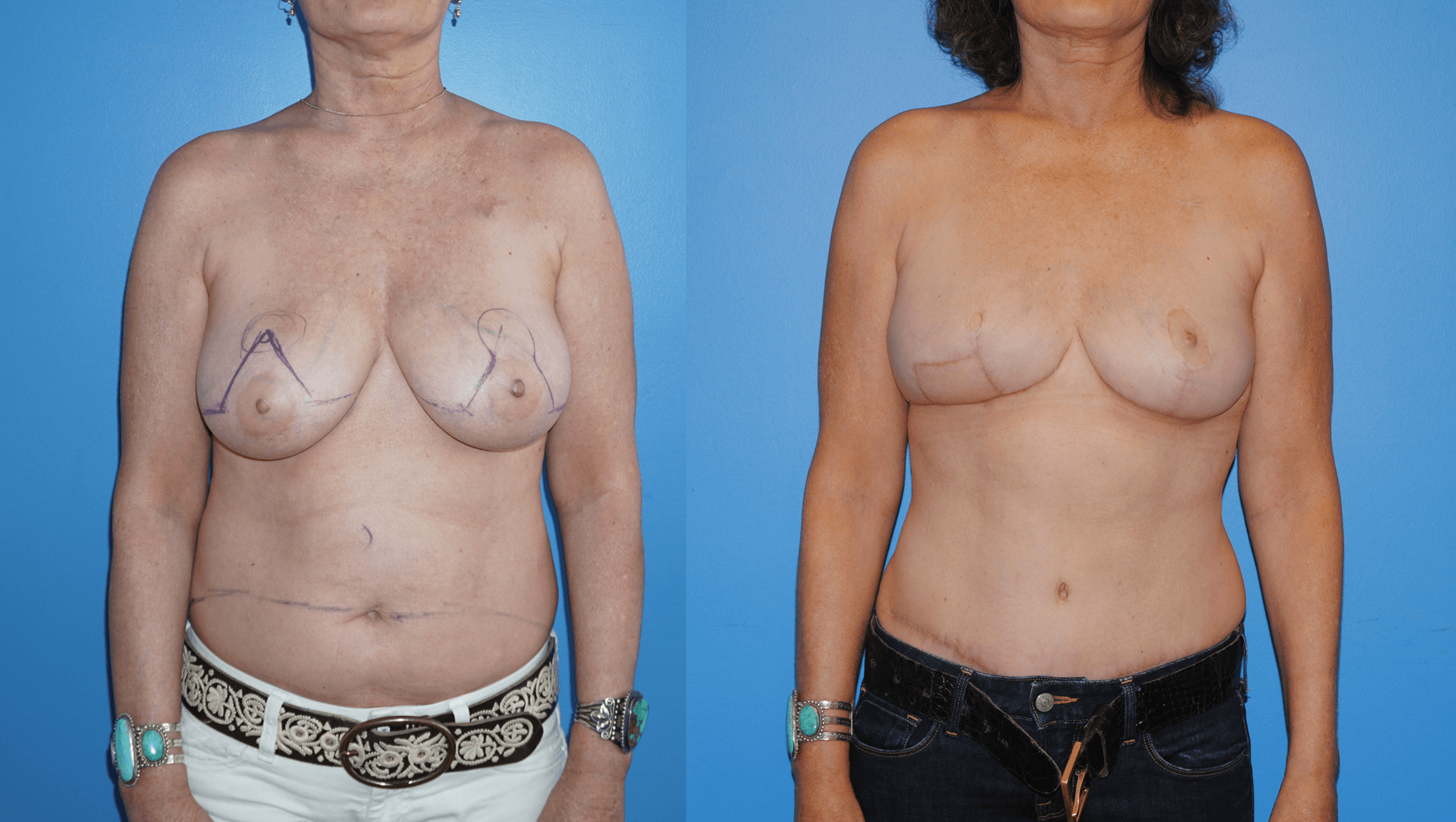
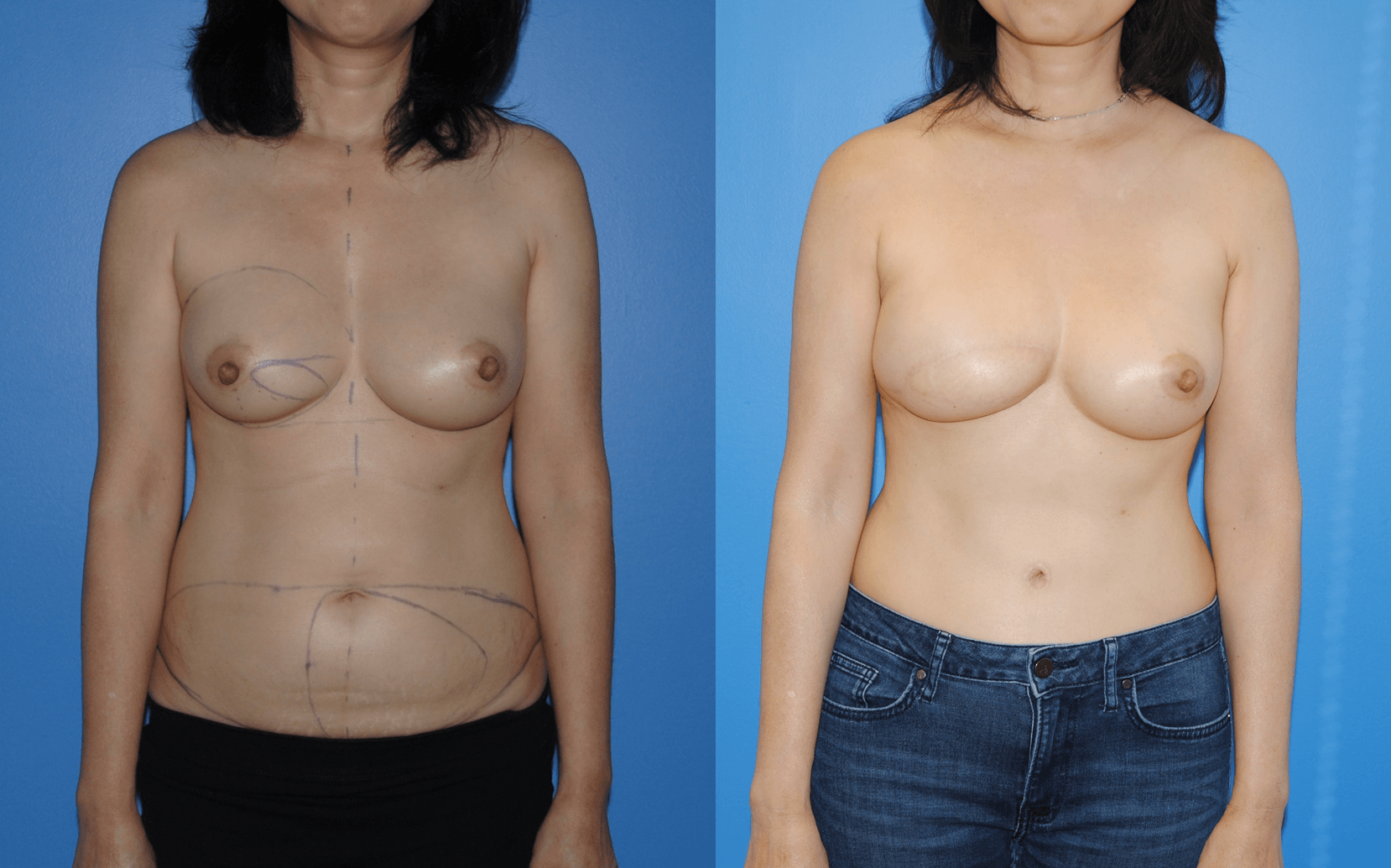
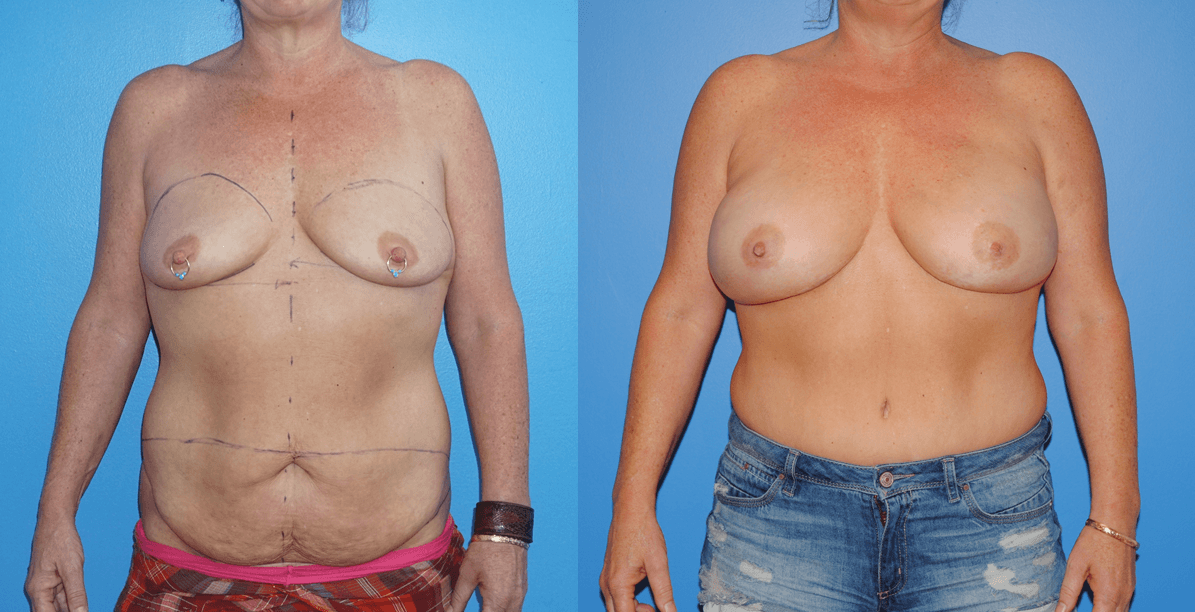
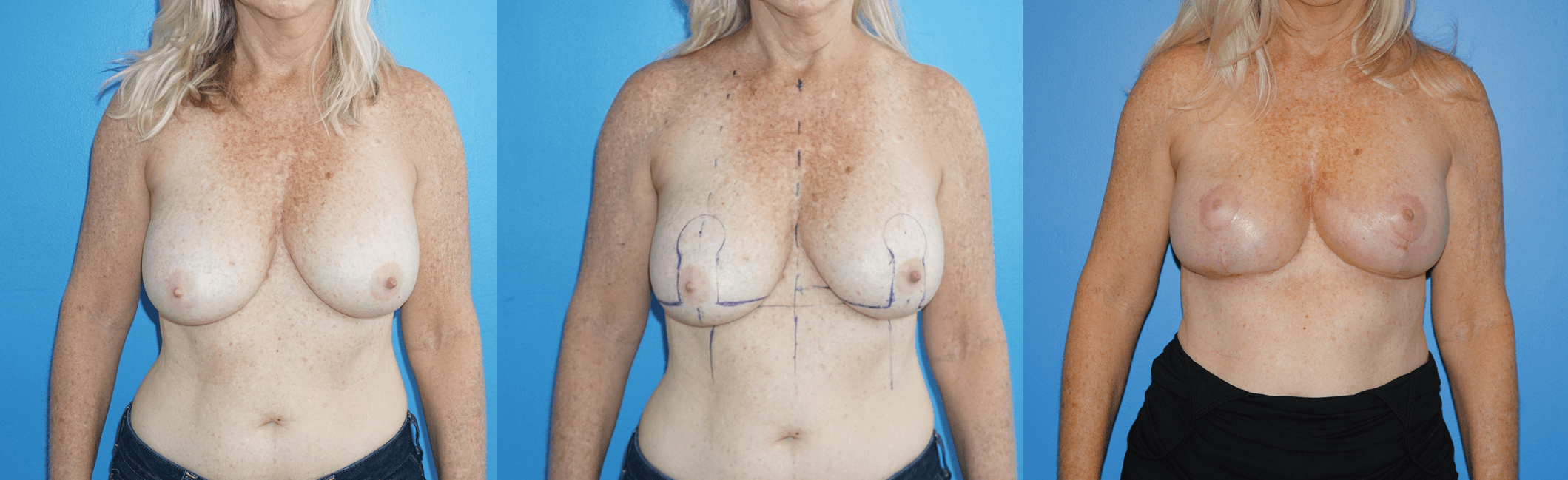
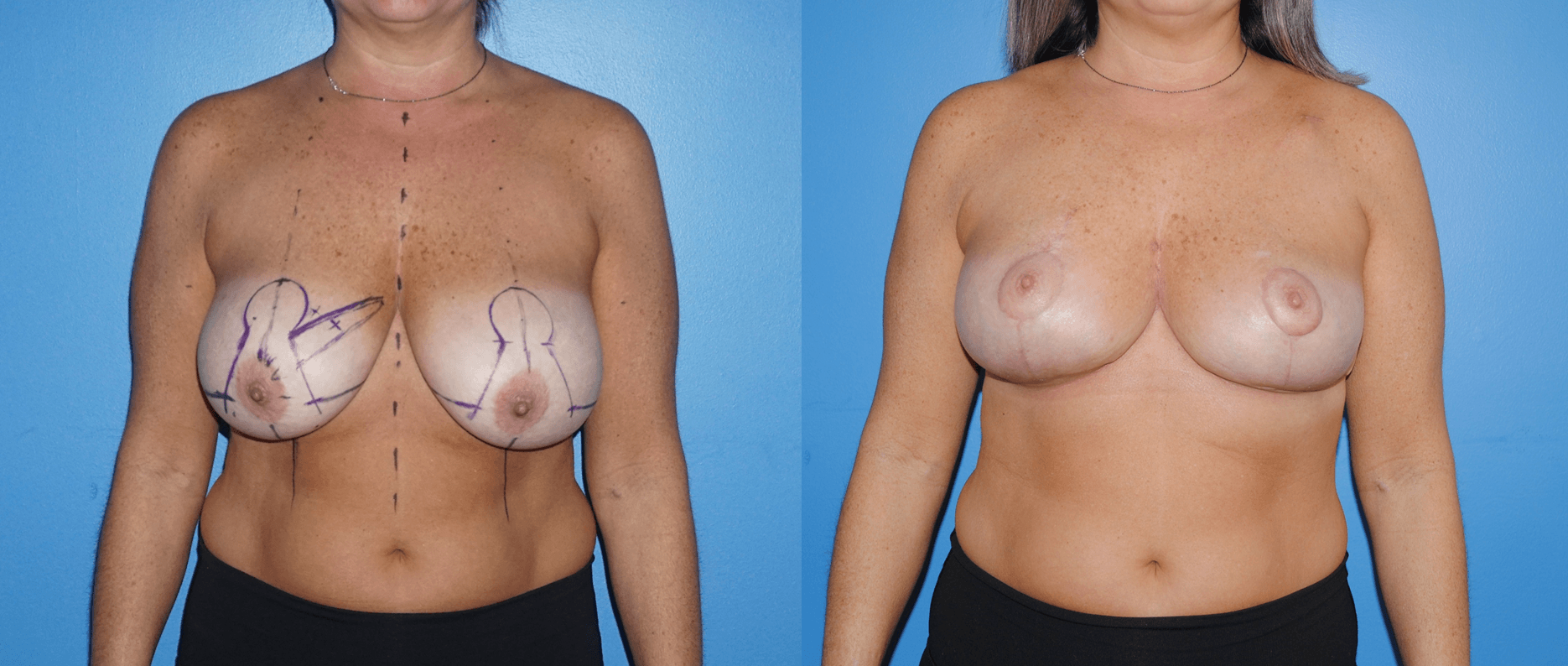
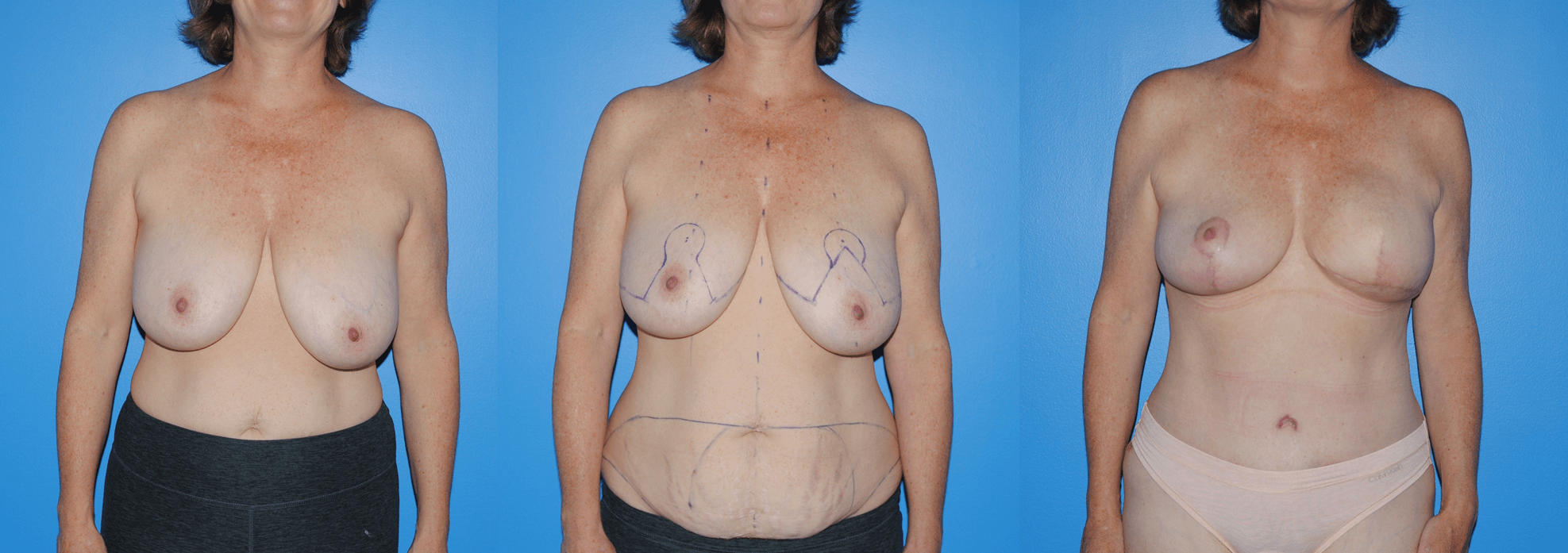
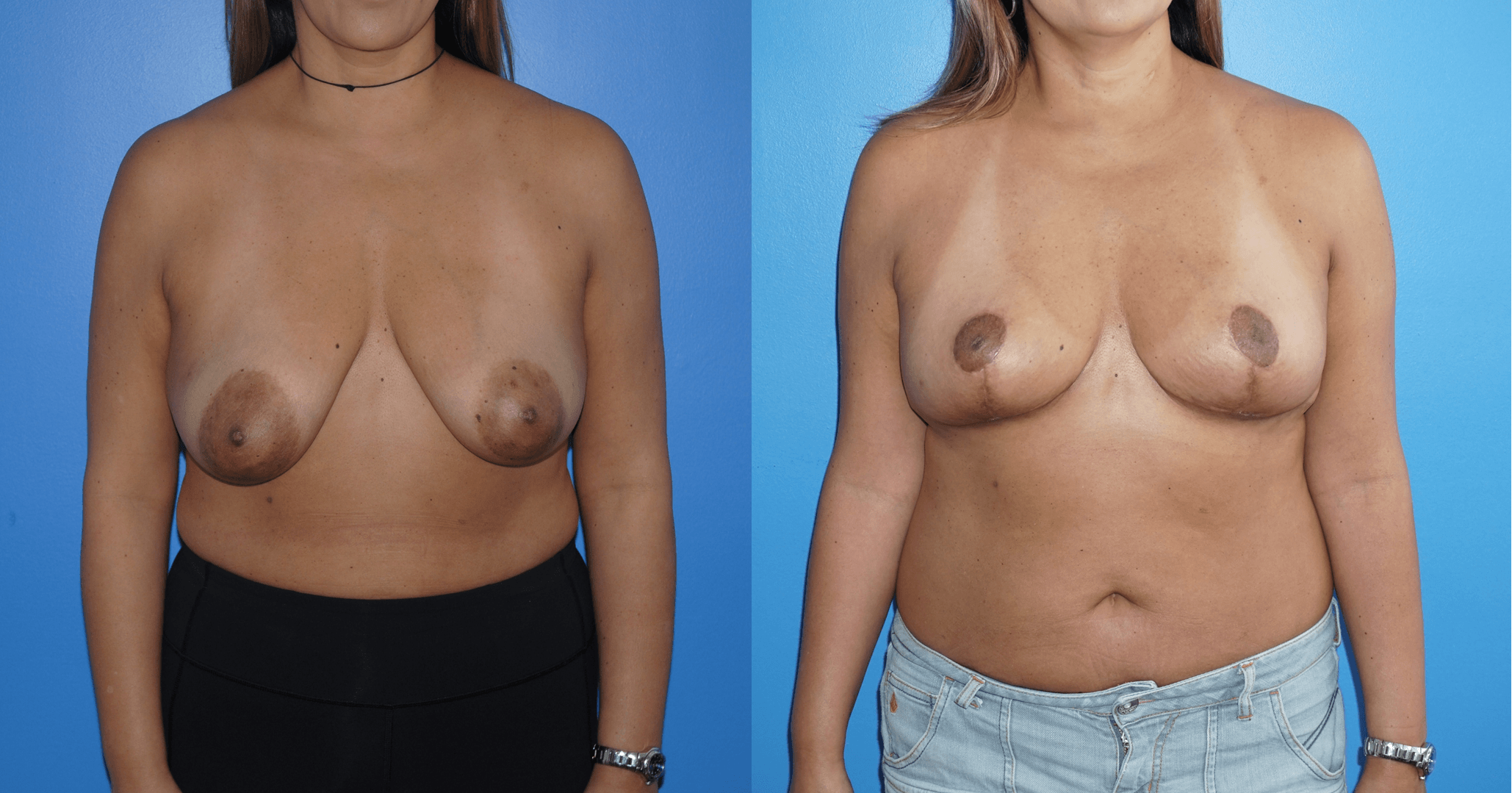
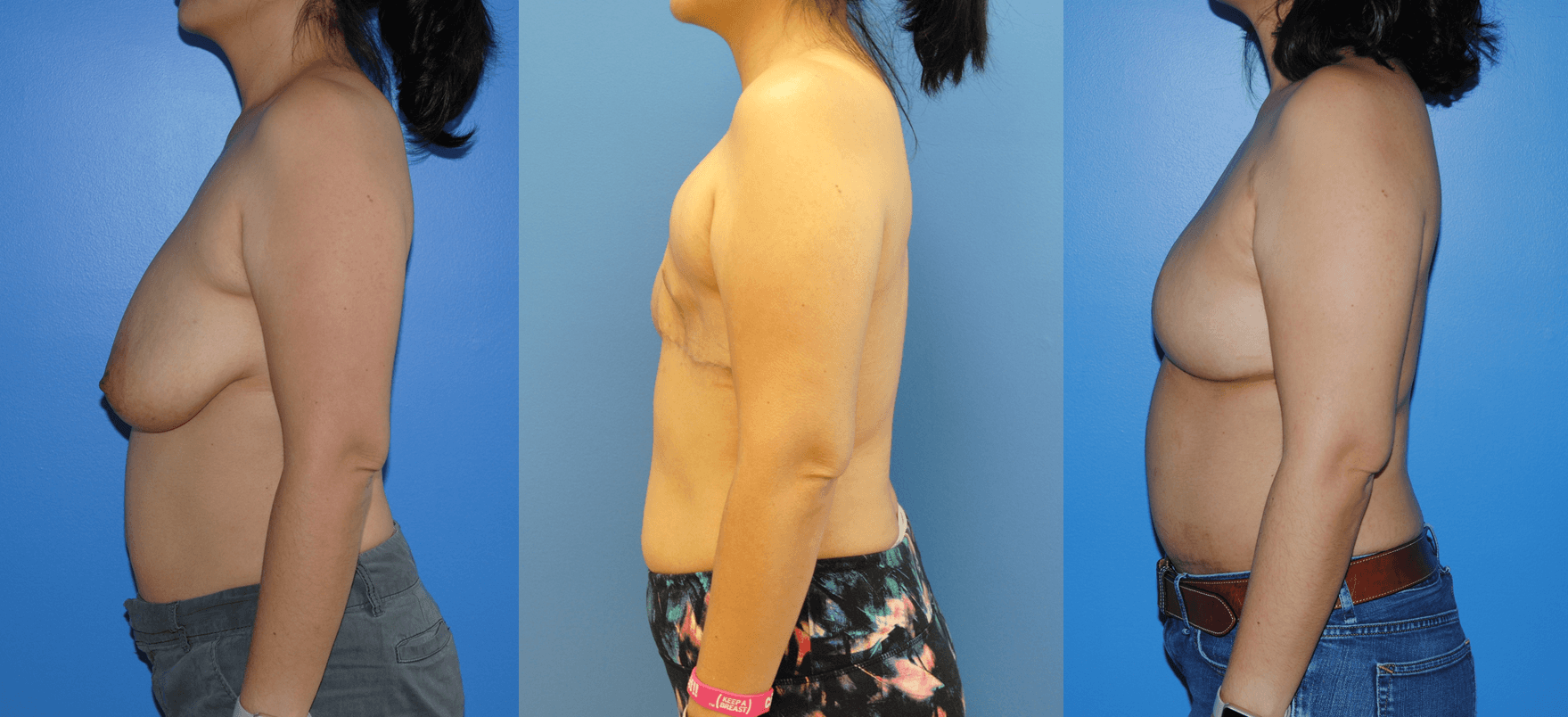There are several oncoplastic techniques that are used to reconstruct the breast following lumpectomy for breast cancer. These oncoplastic techniques can be utilized in conjunction with DIEP flap reconstruction for mastectomy in sequence. Patients can undergo lumpectomy for breast cancer with oncoplastic reconstruction. The staging of the lumpectomy and oncoplastic reconstruction can place a ptotic nipple areola complex in a…