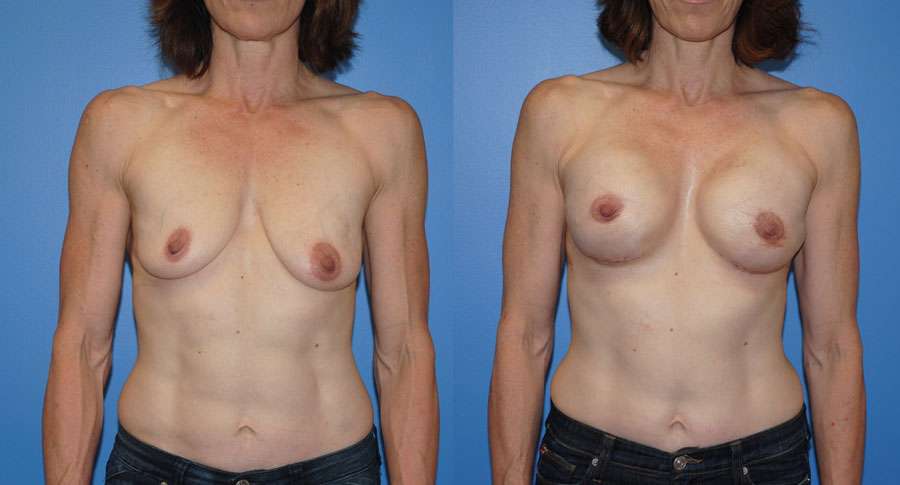
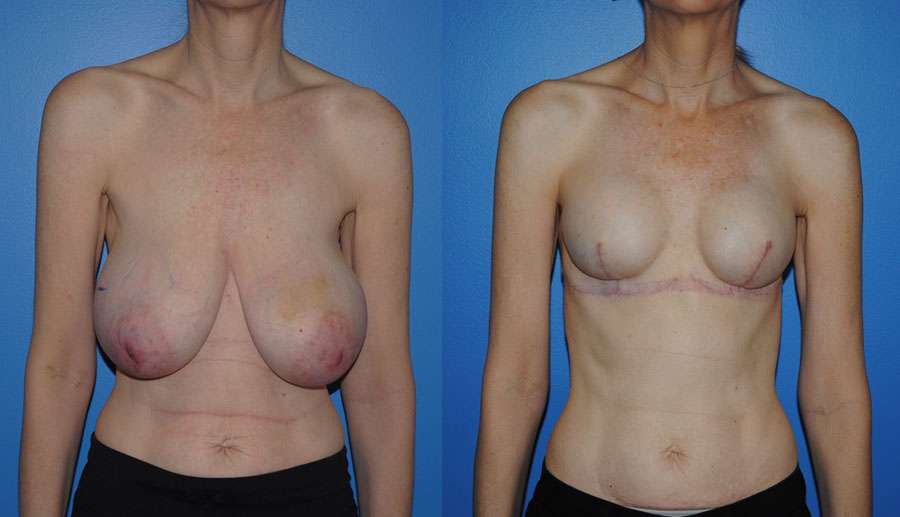
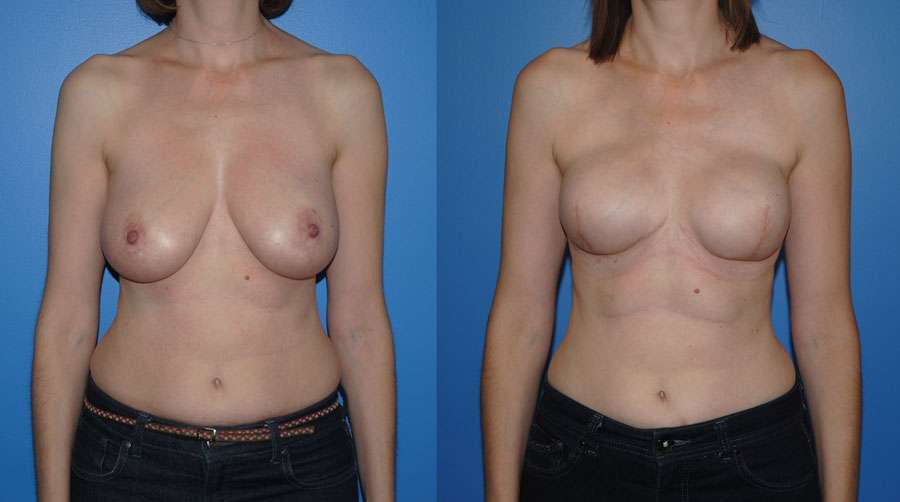
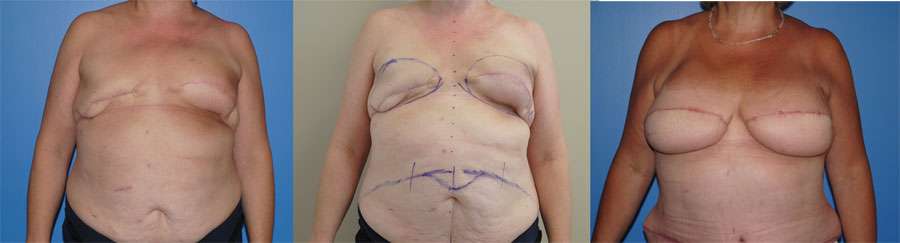
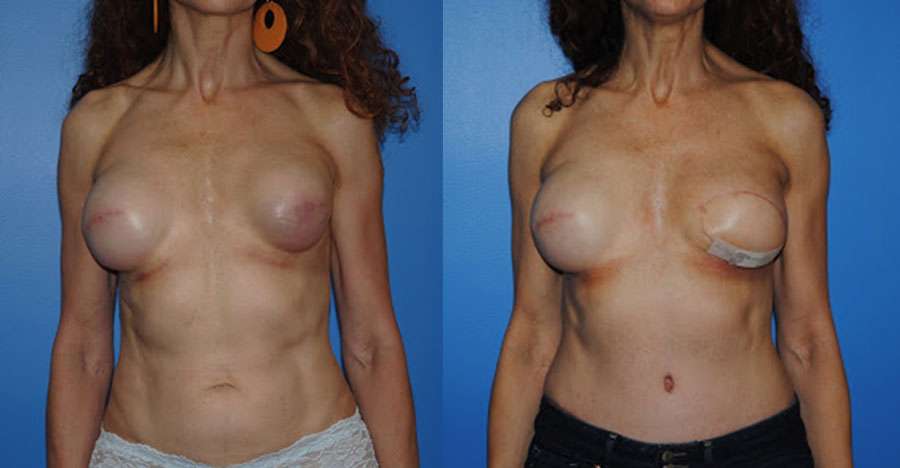
Breast reconstruction following mastectomy is very common. Breast reconstruction often has a better result when the nipple areola complex is preserved. In patients who do not have a ptotic breast, the mastectomy can often be performed from an infra-mammary incision. At the time of the mastectomy, a tissue expander is placed. After the skin has healed the expander is removed…