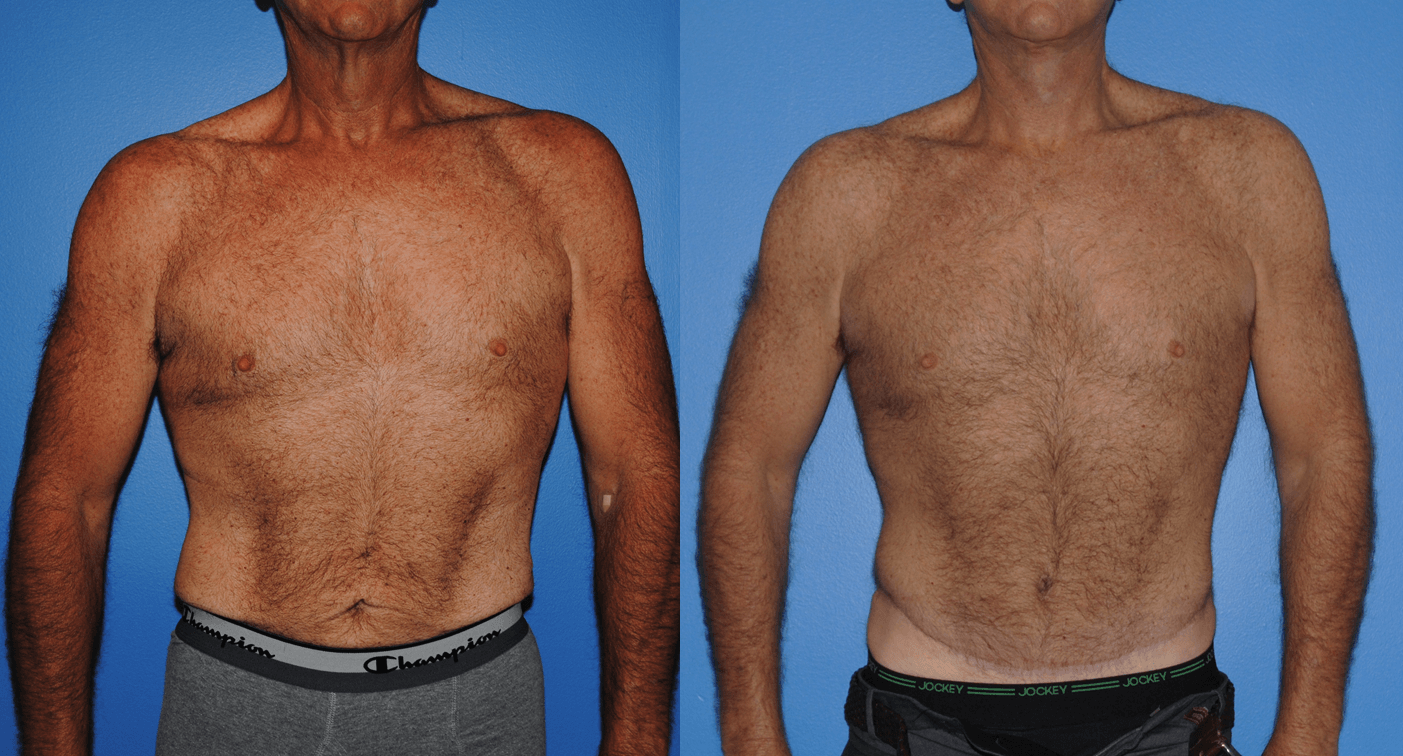
Abdominoplasty procedures are becoming more common in men these days. Men often go to the gym to lift weights or increase their amount of cardiac exercise to lose weight. The resulting excess skin that men accumulate often does not dissipate without a skin resection. That is, the abdominoplasty procedure in men is typically a skin excision only and does not…